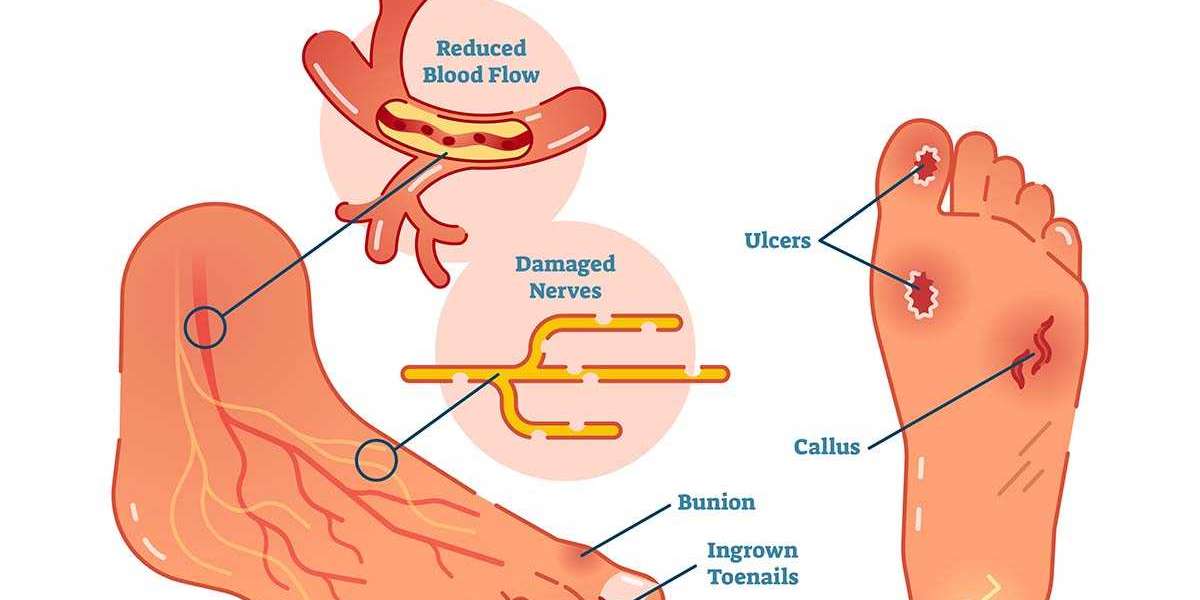
According to a report published by the American Diabetes Association, 19% to 34% of patients suffering from diabetes are likely to develop diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) in their lifetime. With reports suggesting that the yearly incidence of foot ulcers ranges from 1.9% to 4.0%, and in some cases as high as 5.0% to 7.5%, the global impact of this condition is significant. Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Analysis The prevalence of diabetic foot ulcers has surged in recent years, with the number of affected individuals rising from 9.1 million to 26.1 million globally. This alarming trend underscores the urgent need for innovative and effective treatments. As such, several companies and research institutions are heavily investing in the development of solutions to address diabetic foot ulcers, which continue to be one of the most common and serious complications associated with diabetes.
ulcers drug pipeline, focusing on ongoing research, emerging treatments, key players in the market, and the impact of COVID-19 on this growing healthcare challenge.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/diabetic-foot-ulcers-drug-pipeline-analysis/requestsample
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Overview
Diabetic foot ulcers are chronic wounds that often result from neuropathy and poor circulation, and they can lead to severe complications, including infections and amputations. These ulcers are particularly challenging to treat because of their high recurrence rates, the presence of multiple underlying conditions (such as diabetes-related neuropathy, vascular disease, and infection), and the difficulty in promoting wound healing.
Current Treatment Landscape
Traditional treatments for diabetic foot ulcers include wound care management, infection control, debridement (removal of dead tissue), and surgical interventions. However, these methods are not always sufficient, particularly for patients with severe or recurrent ulcers. As a result, there has been a growing interest in drug-based therapies that can accelerate wound healing, reduce the risk of infection, and address the underlying causes of the ulcers.
The drug pipeline for diabetic foot ulcers includes several promising therapies that focus on wound healing, pain management, infection prevention, and even regenerative medicine. Key classes of drugs in the pipeline include:
- Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Agents: To prevent or treat infections that can complicate foot ulcers.
- Growth Factors and Cytokines: These aim to stimulate tissue regeneration and improve wound healing.
- Stem Cell Therapies and Tissue Engineering: Novel approaches that focus on regenerative medicine to promote healing and tissue repair.
- Immunomodulators: These drugs are designed to modulate the immune response to reduce inflammation and promote tissue repair.
- Gene Therapies: Targeting genetic factors that contribute to impaired wound healing.
Key Drug Classes in Development
- Growth Factors and Platelet-Derived Growth Factors: These substances help accelerate tissue regeneration and have shown promise in improving healing rates in clinical trials.
- Bioengineered Skin Substitutes: These products are designed to replace or augment the damaged skin and stimulate healing.
- Advanced Dressings: In addition to traditional wound care products, there is increasing interest in advanced wound dressings that incorporate drugs or antimicrobial agents.
The focus on innovative drug development and new treatments is evident, with several major players and small biotech firms entering the diabetic foot ulcer space.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/diabetic-foot-ulcers-drug-pipeline-analysis
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Dynamics
Market Drivers
The increasing prevalence of diabetes globally, coupled with the rising incidence of diabetic foot ulcers, is driving the demand for new treatments. Additionally, the high costs associated with treating diabetic foot ulcers, including hospitalizations, surgeries, and wound care, are pushing healthcare systems to seek more effective, cost-efficient therapies.
Key drivers of innovation in the diabetic foot ulcer drug pipeline include:
- Rising Global Diabetes Rates: The global diabetes epidemic continues to fuel the demand for treatments aimed at managing diabetic foot ulcers.
- Unmet Medical Need: Current treatments often fail to address the root causes of diabetic foot ulcers, making the development of new therapies a priority.
- Regenerative Medicine: The advent of regenerative medicine techniques such as stem cell therapy and gene therapy has opened up new avenues for treating chronic wounds and promoting tissue regeneration.
Market Challenges
Despite the promising developments in the pipeline, there are several challenges facing the development of effective treatments for diabetic foot ulcers. These challenges include:
- Regulatory Hurdles: Getting approval for new drug treatments can be a lengthy and costly process, particularly for novel therapies like stem cell treatments.
- Cost of New Therapies: Advanced therapies, such as biologics and regenerative treatments, can be expensive, raising concerns about affordability and accessibility for patients.
- Treatment Resistance: As with other chronic diseases, patients with diabetic foot ulcers may develop resistance to certain treatments, especially antibiotics.
External Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Analysis Trends
Several trends are shaping the future of the diabetic foot ulcers drug pipeline:
Focus on Regenerative Medicine: Stem cell-based therapies, tissue-engineered products, and gene therapies are emerging as potential game-changers in diabetic foot ulcer treatment. These therapies aim to repair or replace damaged tissues, thereby accelerating healing.
Advanced Wound Dressings: Companies are developing advanced dressings that are not only capable of protecting wounds but also delivering drugs directly to the site of the ulcer. These dressings can improve healing rates and reduce the risk of infection.
Combination Therapies: There is increasing interest in combination therapies that combine traditional wound care with novel drug treatments to enhance healing. For instance, combining growth factors with antimicrobial agents to promote tissue regeneration while preventing infection.
Personalized Medicine: As more is learned about the underlying molecular mechanisms of diabetic foot ulcers, personalized treatments based on the patient’s unique genetic and physiological profile may become more common.
Emerging Markets: The growing prevalence of diabetes in emerging markets such as Asia and Africa is expected to drive demand for affordable, effective treatments for diabetic foot ulcers.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Segmentation
The diabetic foot ulcer drug pipeline can be segmented into several key categories based on the type of treatment, including:
1. Wound Healing Therapies
These treatments aim to stimulate tissue regeneration and accelerate the healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Growth factors, cytokines, and bioengineered skin substitutes are some of the most promising therapies in this category.
2. Infection Control
Antibiotics, antimicrobial agents, and immunomodulators are commonly used to control or prevent infections in diabetic foot ulcers. Since infections can worsen the condition and lead to complications, effective infection control is critical for successful treatment.
3. Pain Management
Pain is a significant concern for patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Drugs that target neuropathic pain, such as antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and analgesics, are essential for improving patient quality of life.
4. Stem Cell and Regenerative Therapies
Stem cells and tissue engineering approaches are being developed to regenerate damaged tissue and promote faster healing. These therapies hold significant promise for patients with chronic or non-healing ulcers.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Growth
The diabetic foot ulcer drug pipeline is growing rapidly, with numerous clinical trials underway to test new treatments. Investment in the development of new drugs is expected to increase significantly over the next decade, as the global prevalence of diabetes continues to rise.
Several therapies are progressing through clinical stages, with some nearing market approval. Growth factors, stem cell therapies, and bioengineered skin substitutes are expected to dominate the market in the coming years, as they offer the potential for long-term, sustainable healing.
Recent Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Market
The market for diabetic foot ulcer drugs is expanding as the number of affected individuals increases. In 2023, the global diabetic foot ulcer treatment market was valued at approximately USD 2.7 billion, with projections to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6.2% from 2024 to 2032. Key drivers of market growth include:
- The increasing incidence of diabetes and diabetic complications.
- The rising demand for advanced wound care and regenerative medicine.
- The growing investment by pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms in the development of novel therapies.
Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline Scope
The scope of the diabetic foot ulcers drug pipeline extends across various treatment categories, including wound care, infection control, pain management, and regenerative medicine. As new therapies emerge, the scope of available treatments for diabetic foot ulcers will expand, offering more options for patients and healthcare providers alike.
The Impact of COVID-19 on the Diabetic Foot Ulcer Drug Pipeline
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the development and availability of treatments for diabetic foot ulcers. On the one hand, the pandemic has slowed down clinical trials and delayed the approval of new drugs. On the other hand, the crisis has underscored the importance of addressing chronic health conditions like diabetes and its complications, including foot ulcers.
The focus on healthcare infrastructure and the urgent need for new treatments post-pandemic may lead to an acceleration in the approval and distribution of innovative drugs for diabetic foot ulcers.
Key Players in the Diabetic Foot Ulcers Drug Pipeline
Several pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms are playing a critical role in the development of treatments for diabetic foot ulcers. Some of the key players in this space include:
- Cytora Ltd.
- Anterogen Co., Ltd.
- ProgenaCare Global, LLC
These companies are working on a range of innovative therapies, including regenerative treatments, growth factor-based products, and novel antimicrobial agents, to address the unmet needs in diabetic foot ulcer management.
FAQ
Q1: What is the global market size for diabetic foot ulcer treatments?
The global market for diabetic foot ulcer treatments was valued at approximately USD 2.7 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% from 2024 to 2032.
Q2: What are the main causes of diabetic foot ulcers?
Diabetic foot ulcers are primarily caused by peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage) and poor circulation, which make it difficult for wounds to heal properly.
Q3: How are stem cell therapies being used for diabetic foot ulcers?
Stem cell therapies are being developed to promote tissue regeneration and accelerate the healing of diabetic foot ulcers, especially in chronic or non-healing wounds.
Q4: What are the most promising drug classes in the diabetic foot ulcer pipeline?
Promising drug classes include growth factors, cytokines, stem cell-based treatments, antimicrobial agents, and bioengineered skin substitutes.