In the ever-evolving landscape of modern dentistry, the role of the dental hygienist has transformed from a routine caretaker to a pivotal player in comprehensive oral health management. As dental practices adapt to new technologies, methodologies, and patient expectations, dental hygienists are uniquely positioned to lead the charge in enhancing care quality, improving patient outcomes, and driving innovations within the field. This article explores how dental hygienists can elevate their roles from routine practitioners to remarkable contributors in contemporary dentistry, with a particular focus on practices such as those run by a dentist in East Finchley.
The Evolving Role of Dental Hygienists
Historically, dental hygienists have been seen primarily as preventive care providers, focused on tasks such as teeth cleaning, scaling, and polishing. While these functions remain essential, the scope of their role has expanded significantly. Today’s dental hygienists are increasingly involved in a wide range of activities that require advanced knowledge, critical thinking, and clinical skills. They are becoming integral members of the dental team, contributing to patient education, treatment planning, and the implementation of cutting-edge technologies.
Embracing Advanced Technologies
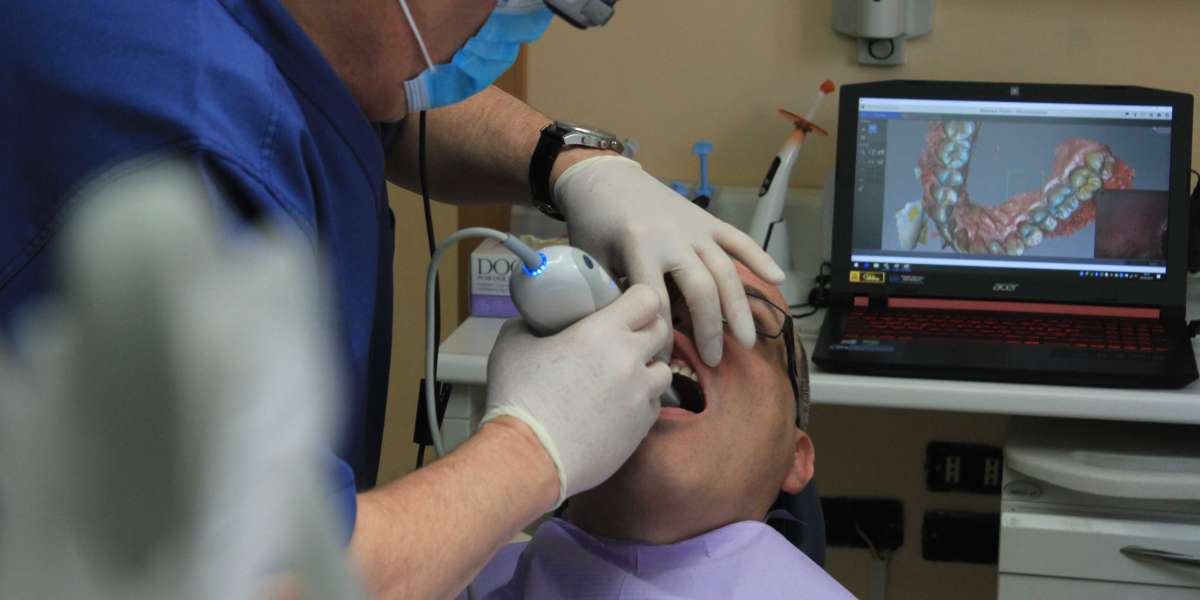
One of the most significant shifts in modern dentistry is the integration of advanced technologies. Dental hygienists are at the forefront of utilizing these tools to enhance patient care and streamline clinical procedures. For instance:
Digital Radiography: Advanced imaging techniques, such as digital radiography, offer enhanced diagnostic capabilities and reduced radiation exposure. Dental hygienists must be adept at using these technologies to assess and monitor patients’ oral health more effectively.
Intraoral Cameras: These devices allow for real-time visualization of the oral cavity, facilitating better patient communication and more accurate diagnostics. Proficiency with intraoral cameras enables dental hygienists to provide detailed explanations and engage patients in their care decisions.
Laser Therapy: The use of lasers in dental hygiene procedures—such as periodontal therapy and caries removal—has revolutionized treatment approaches. Hygienists trained in laser technology can offer minimally invasive procedures with improved patient comfort and outcomes.
Enhancing Preventive Care
The transition from routine to remarkable in dental hygiene also involves a deeper focus on preventive care. Modern dental hygienists are tasked with not just treating but also preventing oral diseases through comprehensive care strategies:
Personalized Risk Assessments: By conducting thorough risk assessments, dental hygienists can identify factors that predispose patients to oral diseases. This proactive approach enables the development of tailored preventive strategies, such as customized home care regimens and targeted education.
Behavioral Counseling: Dental hygienists are increasingly involved in counseling patients on lifestyle modifications that impact oral health, such as diet, smoking cessation, and effective brushing techniques. Their role in behavioral counseling is critical for achieving long-term health improvements.
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Effective preventive care often requires collaboration with other healthcare providers. Dental hygienists in East Finchley can enhance patient outcomes by working closely with physicians, dietitians, and other specialists to address systemic health issues that affect oral health.
Advancing Professional Development
To truly elevate their roles, dental hygienists must commit to ongoing professional development. Staying current with emerging research, treatment modalities, and best practices is essential for maintaining a high standard of care. Opportunities for advanced education and specialization—such as certifications in periodontal therapy, public health, or dental sleep medicine—enable hygienists to expand their expertise and contribute more significantly to their practices.
Leading in Patient Education
Education is a cornerstone of modern dental hygiene practice. Dental hygienists have the opportunity to empower patients with knowledge about their oral health and treatment options. By providing clear, evidence-based information and engaging in meaningful conversations, they help patients make informed decisions and adhere to recommended care plans.
Conclusion
The role of dental hygienists in modern dentistry extends far beyond traditional preventive care. By embracing advanced technologies, focusing on personalized preventive strategies, committing to professional development, and leading in patient education, dental hygienists can elevate their practice from routine to remarkable. As integral members of the dental team, they have the potential to drive significant improvements in patient outcomes and contribute to the ongoing evolution of dental care. Through their dedication and expertise, dental hygienists are redefining their roles and shaping the future of dentistry.